Sterling™-LWB+ WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.2 Modules
Overview
New: M.2-2230 module, part # 453-00141!
Ezurio's (formerly Laird Connectivity) new Sterling™-LWB+ WiFi 4 with Bluetooth 5.2 module, based upon the Infineon AIROC™ CYW43439 chipset, is the latest member of the successful Sterling-LWB radio family. This embedded module series is available as a System-in-Package (SIP) and two certified module versions, supporting either an on-board chip antenna or a MHF connector for an external antenna. It is designed to meet the demands of medical and industrial IoT connectivity, and is mechanically and pin compatible with our Sterling-LWB module as an upgrade path for existing customers.
The Sterling-LWB+ contains a fully featured WiFi 4 radio, enabled with our industry-leading software drivers and support. The secure, high performance SDIO solution provides easy integration with any Linux or Android based system. It is designed for IoT from the start: fully certified, easy to integrate, and is the fastest route to the market for wireless IoT applications.
- Compatible: Our Linux Backports package supports many Linux kernels.
- Reliable: High quality drivers and extended product life support.
- Robust: Rich feature-set including 802.11b/g/n WiFi and Dual-Mode Bluetooth.
- Secure: Supports the latest WPA2/WPA3 Enterprise security standards.
- Industrial Temp: Supports -40 to +85°C industrial temperature operation
Premium WiFi Advantage
The road to bringing wireless to your product is perilous and long – but it doesn’t have to be. These are the pillars of our value as a partner and provider: Excellence in development across hardware and software, delivered with industry-best support and deployed around the world in the markets that drive your business success.
Ezurio is an Infineon Premium Partner
Ezurio is honored to be approved as an Infineon Premium Partner. A partnership which leverages Infineon’s AIROC™ Wi-Fi chipsets and ModusToolbox™ solutions combined with Ezurio's superior software enablement and integration support.

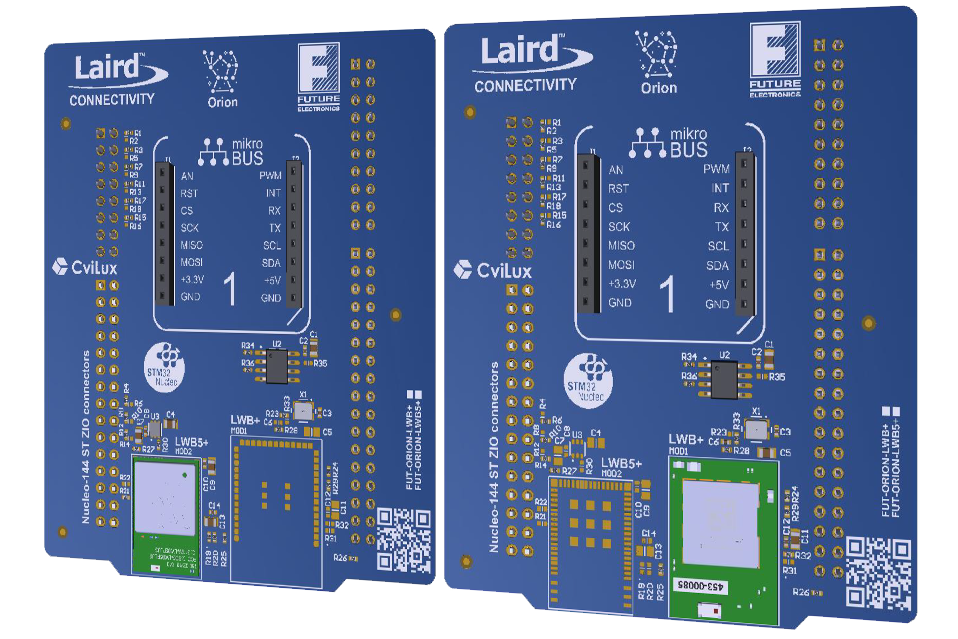
Orion Development Boards
A collaboration Between Future Electronics and Ezurio
The Orion development boards are designed by Future Electronics to showcase our Sterling™-LWB+ (Infineon CYW43439) and Sterling-LWB5+ (Infineon CYW4373E) embedded Wi-Fi modules, which are based on the Infineon AIROC chipsets. The Orion design makes application development and evaluation easy. Both boards support the ST Micro Nucleo-144 adaptor for easy evaluation with STM32 MCUs and MikroBus header that enables further expansion. Both of our modules are supported by Infineon’s STM32 Connectivity Expansion Pack 1.5.1 for STM32CubeMX tool, for ease of application development.
Click below to request a kit from Future Electronics.
Specifications
Bluetooth 5.2
21 x 15 x 4 mm (PCB Module)
22 x 30 x 2.73 (M.2 Module)
HCI HS-UART, PCM (Bluetooth)
| Part Number | Additional Description | Antenna Type | Bulk or Single | Chipset (Wireless) | Frequency Range (Max) | Frequency Range (Min) | Logical Interfaces | OS/Software | Product Type | System Architecture | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 453-00083CBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, SiP Module | Antenna Trace | Bulk, Cut Tape | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00084CBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, PCB Module with MHF4 Connector | MHF4 Connector | Bulk, Cut Tape | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00085CBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, PCB Module with Chip Antenna | Chip Antenna | Bulk, Cut Tape | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00083RBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, SiP Module | Antenna Trace | Bulk, Tape and Reel | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00085RBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, PCB Module with Chip Antenna | Chip Antenna | Bulk, Tape and Reel | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00084RBuy Now | Sterling LWB+, PCB Module with MHF4 Connector | MHF4 Connector | Bulk, Tape and Reel | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 453-00141Buy Now | Sterling LWB+, M.2 Module | MHF4 Connector | Infineon CYW43439 | 2400 MHz | 2400 MHz | SDIO, HS-UART, PCM | Linux | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11bgn, Bluetooth 5.2 |
Development Kits
-
/filters:background_color(white)/2021-10/453-00084.png)
453-00084-K1
Additional DescriptionSterling LWB+ Development Kit, MHF4 ConnectorAntenna TypeMHF4 Connector -
/filters:background_color(white)/2021-10/453-00085.png)
453-00085-K1
Additional DescriptionSterling LWB+ Development Kit, Chip AntennaAntenna TypeChip Antenna
Documentation
Certified Antennas
Is there a way to change the TX power in Infineon modules, IF573, LWB(5) and LWB(5)+ series?
There is no way without custom CLM blob and/or custom NVRAM which would require a custom firmware for individual customer and this is not the part that we will support by standard process.
In order to enable gpioset feature on a Linux platform, which packages need to be added by yocto?
Need to add libgpiod, libgpiod-dev and libgpiod-tools.
libgpiod containing libgpiod.so* files
libgpiod-dev containing /usr/include for the header files and /usr/lib for the shared lib's solink file and corresponding pkgconfig metadata.
libgpiod-tools containing gpiodetect, gpioget, …
What is the ITU code for Wi-Fi with WiFi/BT combo module?
Mode | ITU-Code |
2.4-2.4835GHz | - |
802.11b_Nss1,(1Mbps)_1TX | 12M2G1D |
802.11g_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M7D1D |
802.11n HT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M9D1D |
802.11n HT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M6D1D |
5.15-5.25GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M6D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
5.25-5.35GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M6D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
5.47-5.725GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M7D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M8D1D |
5.725-5.85GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M7D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
What is the ITU code for BT with WiFi/BT combo module?
Mode | ITU-Code |
2.4-2.4835GHz | - |
BT-BR(1Mbps) | 889KF1D |
BT-EDR(3Mbps) | 1M22G1D |
BT-LE(1Mbps) | 1M05F1D |
What is the Orion Development Board?
The Orion Development Board is a collaboration between Ezurio and Future Electronics to showcase our Sterling-LWB+ and our Sterling-LWB5+.
There are two variants of the Orion Development Board:
- FUT-ORION-LWB+ featuring:
- Ezurio Sterling-LWB+
- ST Micro Nucleo-144 adaptor to support the STM32 MCUs
- SPI flash on board
- MikroBus header for expansion
- FUT-ORION-LWB5+ featuring:
- Ezurio Sterling-LWB5+
- ST Micro Nucleo-144 adaptor to support the STM32 MCUs
- SPI flash on board
- MikroBus header for expansion
The Orion boards make application development and evaluation easy. Both boards support the ST Micro Nucleo-144 adaptor for easy evaluation with STM32 MCUs and MikroBus header that enables further expansion. Both modules are supported by Infineon’s STM32 Connectivity Expansion Pack 1.5.1 for STM32CubeMX tool, for ease of application development.
How to activate SDIO on the M2 slot of the i.MX8 LPDDR4 DVK of NXP
After building a default image for the NXP i.MX8 LPDDR4 DVK device tree is such that M2 slot provides PCIe connectivity.
However SDIO device tree is generated and available in the image.
The parameter "fdtfile=" in U-Boot needs to be changed.
Change "fdtfile=imx8mp-evk-revb4.dtb" to "fdtfile=imx8mp-evk-usdhc1-m2.dtb" by:
u-boot=> setenv fdtfile imx8mp-evk-revb4-usdhc1-m2.dtb
u-boot=> saveenv
Reference:
root@imx8mp-lpddr4-evk:~# ls /dev/mmc*
/dev/mmcblk2 /dev/mmcblk2boot0 /dev/mmcblk2boot1 /dev/mmcblk2p1 /dev/mmcblk2p2 /dev/mmcblk2rpmb
root@imx8mp-lpddr4-evk:~# mount /dev/mmcblk2p1 /media/
root@imx8mp-lpddr4-evk:~# ls /media | grep usdhc
imx8mp-evk-revb4-usdhc1-m2.dtb
imx8mp-evk-usdhc1-m2.dtb
Do any of your Wi-Fi radios work with ST Microprocessors?
If you are using any of these ST Microprocessors in your application, you can pair either the Sterling-LWB5+ or the Sterling-LWB+ using ST Micro's stm32cubeide.
- STM32H7xx
- STM32L5xx
- STM32U5xx
- STM32H5xx
Do any of your Wi-Fi radios work with a PSOC6?
If you are using an Infineon PSOC6 Microprocessor in your application you can pair either the Sterling-LWB5+ or the Sterling-LWB+ using Infineon's ModusToolbox software.
Does the LWB+ Work with an RTOS?
While the Sterling-LWB+ does not have an onboard MCU, if you are using a PSOC6 or certain ST Microprocessors in your application you can use the Sterling-LWB+.
PSOC6
The Sterling-LWB+ can be used with the Infineon PSOC6 through their ModusToolbox software.
ST Micro
The Sterling-LWB+ can be used with stm32cubeide on these Microprocessors:
- STM32H7xx
- STM32L5xx
- STM32U5xx
- STM32H5xx
I am planning on using kernel 6.1 (mickledore), is there anything I need to be aware of?
There was a change in kernel 5.19 and higher, lrd-11 is built against the kernel 6.1 kernel backports), where there is a requirement to add cfg80211 to your image as a module (m) in the base platform kernel configuration. It must not be left out and must not be included as built-in (y). Networking support->Wireless->cfg80211 - wireless configuration API
Do I need to do anything differently in lrd-11 release?
Do I need to do anything differently in lrd-11 release?
There was a change in kernel 5.19 and higher, lrd-11 is built against the kernel 6.1 kernel backports), where there is a requirement to add cfg80211 to your image as a module (m) in the base platform kernel configuration. It must not be left out and must not be included as built-in (y).
- Networking support->Wireless->cfg80211 - wireless configuration API
Why I am seeing an error while trying to build lrd-11 in Yocto?
I am seeing an error: error: 'struct net_device' has no member named 'ieee80211_ptr'
while trying to build the lrd-11.0 release in Yocto.
This is due to a change in kernel 5.19 and higher, (lrd-11.0 is built against 6.1 kernel backports), where there is a requirement to add cfg80211 to your image.
To accomplish this:
- Edit your kernel configuration by entering
bitbake -c menuconfig virtual/kernel - Edit Networking support/Wireless and set cfg80211 to "M" for module
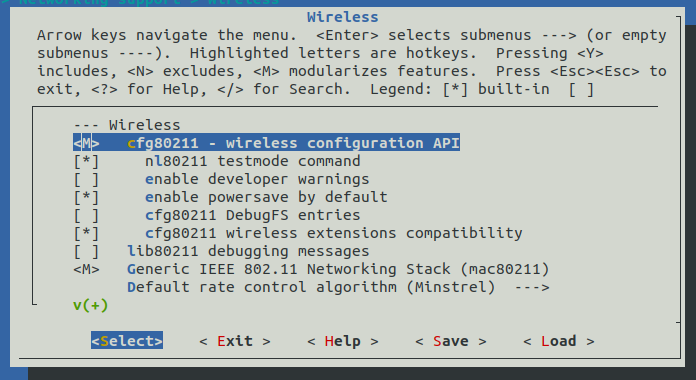
- Save your changes.
- Run your build again.
Do Laird Wifi modules work with OpenWRT?
Yes, Laird Wifi modules can be integrated with OpenWRT like with almost any other Linux operating system.
See Lairds "Guide" Section for an example on how to integrate the Sterling-LWB5+ Wifi/Bluetooth module with OpenWRT on a Raspberry Pi.
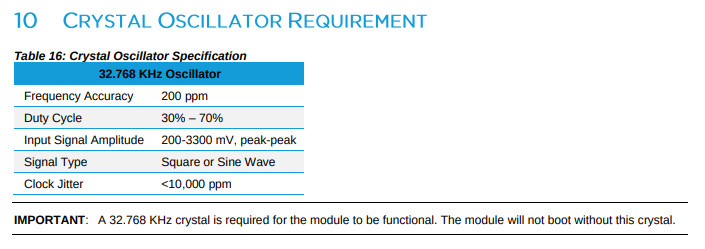
Why and I getting an error in dmesg "brcmfmac: brcmf_sdio_htclk: HT Avail timeout (1000000): clkctl 0x50" when trying to start my Sterling-LWB+ radio?
I am getting an error in dmesg "brcmfmac: brcmf_sdio_htclk: HT Avail timeout (1000000): clkctl 0x50" when trying to start my Sterling-LWB+ radio.
In general, this error occurs when you do not have a 32kHz external oscillator in your design. This is required for the LWB series radios.
From the Sterling-LWB+ Datasheet:
Can I use power save mode for AP mode?
PM mode is ignored when operating as an AP. It is effectively PM=0.
How to support WPA3 Enterprise Suite b 192 by NetworkManager?
The setting would be similar as TLS setup except these two configurations.
802-11-wireless-security.proto wpa3
802-11-wireless-security.key-mgmt wpa-eap-eap-suite-b-192
For example:
nmcli c add type wifi ifname wlo61s0 con-name 'My Wifi Network' \
802-11-wireless.ssid 'My Wifi' \
802-11-wireless-security.key-mgmt wpa-eap-eap-suite-b-192 \
802-11-wireless-security.proto wpa3 \
802-1x.eap tls \
802-1x.identity identity@example.com \
802-1x.ca-cert /etc/cert/ca.pem \
802-1x.client-cert /etc/cert/user.pem \
802-1x.private-key /etc/cert/user.prv \
802-1x.private-key-password the_password
How to support WPA3 Enterprise Suite b 192 by wpa-supplicant configuration?
If you configure Wi-Fi setting by wpa_supplicant, you will need to setup a configuration file such as "/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf", and then execute wpa_supplicant as below command.
wpa_supplicant -Dnl80211 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -i wlan0 -B -ddd
Here is the example of wpa_supplicant.conf to setup "WPA3 Enterprise Suite b 192" network.
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant
#update_config=1
network={
ssid="Cisco_2802_WPA3_Enterprise"
proto=WPA3
key_mgmt=WPA-EAP-SUITE-B-192
ieee80211w=2
pairwise=GCMP-256
group=GCMP-256
group_mgmt= BIP-GMAC-256
eap=TLS
identity=xxxx
ca_cert="/etc/cert/ca.pem"
client_cert="/etc/cert/user.pem"
private_key="/etc/cert/user.prv"
private_key_passwd="password"
phase1=”tls_suiteb=1”
}
Do the LWB series radios support Monitor Mode?
The Sterling-LWB, Sterling-LWB5, Sterling-LWB5+ and the Sterling-LWB+ do not support Monitor Mode. As of 3Q-2023, the
only Laird Radios that support Monitor mode are the 60-SIPT and the 60-2230C.
How do I determine which LRU installer I need?
In the Regulatory Tools package you receive there are many files. The filename structure is:
{radio-type}-{toolchain}-{version}.tar.bz2
For example, the file mfg60n-arm-eabihf-10.135.0.6.tar.bz2 would be for our 60 Series radio running on a system with a GNU Embedded Application Binary Interface (High Float) running version 10.135.0.6 of the Laird firmware.
An easy way to determine your toolchain is to use the command:
ls -l /ld-linux*
Where can I find the Regulatory Test tools for Laird's Wi-Fi products?
For Regulatory Testing you will be required to
load a special firmware to put the radio into "Test Mode". The code
for our Wi-Fi modules is available-by-request by opening a case with our
Support Team at https://www.lairdconnect.com/resources/support.
Does LWBx series support WPA3 OWE?
No, the LWBx series of WiFi/BT modules do not support WPA3 OWE or SAE-PK (Public Key).
How can Lairds LWB-series radios be used with Raspberry Pis and Raspberry Pi OS?
The Sterling-LWBx radios can be used with Raspberry Pis running Raspberry Pi OS.
A module parameter (available from release version 10.54.0.13 on) will have to be used to prevent the module from ideling as OS calls from the mmc driver on RPi will not be answered suitably causing the SDIO communication not to function correctly.
Please reference this tutorial for the 60-series radios and contact Laird for the usage of the above mentioned module parameter for the LWB radios.
https://lairdcp.github.io/guides/Sterling-60-Tutorials/1.0/raspberry-pi-wifi-bt.html
How can I manipulate the power saving settings for Wifi in my Linux environment?
Wifi adapters by default often come up in a power save mode. That is a mode in which the adapter shuts off the network connection in a state of inactivity.
While this is a good way to achieve additional power savings it of course introduces a delay for re-connecting.
To set the mode on or off:
iw wlan0 set power_save on
iw wlan0 set power_save off
To query the current setting issue:
iw wlan0 get power_save
Some systems might require "sudo" in front of the commands to be exectuted.
Jetson TX2 NX Wi-Fi USB is not showing up after a soft reboot
The Jetson TX2 NX does not act the same as the Jetson Nano when providing power to the m.2 slot. The Jetson Nano will automatically toggle PMU_EN, while the TX2 NX will require a manual toggle of the pin in software.
This applies to USB variants, as PCIe variants have a reset built into the PCIe standard.
unknown symbol in dmesg error
On a linux system if the dmesg is reporting an unknown symbol this is usually due to one of the following:
- The backports drivers didn't get compiled against the correct kernel.
- WLAN, CONFIG_BT, and WIRELESS were not removed from the kernel menuconfig.
- backports was compiled with different flags than how the kernel was compiled.
Do your Wi-Fi modules provide a temperature value?
Currently none of our Wi-Fi modules support reading a temperature value.
One important thing to make sure before sending in your device to Laird for country, regulatory or antenna testing.
When you have an agreement with Laird to send in your device for testing of anything around your radio you need to make sure your radio can be set to all necessary test modes.
In order to do that please contact the Laird FAE already known to you or write to Laird at "support@lairdconnect.com" to get in contact with us.
Your FAE will be able to help you determine if your device is fit for testing.
How to set regulation domain in LWB/LWB5/LWB5+ with latest release 8.5.0.7 and later release in Linux platform?
(1) By option regdomain
/etc/modprobe.d/brcmfmac.conf # Sample contents of a brcmfmac.conf file configured for operation in # the United States options brcmfmac regdomain="US"
(2) By device tree
@mmc0 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
bus-width = <4>;
non-removable;
brcmf: wifi@1 {
reg = <1>;
compatible = "brcm,bcm4329-fmac";
laird,regdomain = "US";
};
};
How will Laird handle the FRAG attack announced by Wi-Fi Alliance in 2021 May?
Please refer this blog as below. Laird are currently investigating these issues internally and investigating with the chipset vendors and our internal QA team to establish test scenarios to evaluate the impacted devices.
/resources/blog/frag-attack-wi-fi-putting-pieces-back-together
What are some disadvantages of using AP+STA?
The AP and STA are on the same channel potentially causing disconnections if the STA roams to a different AP. The Sterling-70 has the advantage of dual independent radios that can run on different Wi-Fi channels.
What is the MCS index for Wi-Fi?
MCS stands for Modulation Coding Scheme and is an industry metric index based on Wi-Fi connection parameters between a client and wireless access point. These parameters include modulation type, coding rate, spatial streams, channel width, and guard interval.
What versions of Android are supported by Laird Wi-Fi modules?
This can be found by reviewing the release notes for the specific product on GitHub.
- LWB, LWB5, LWB5+ - Sterling-LWB-and-LWB5-Release-Packages
- Sterling 60 - Sterling-60-Release-Packages
I have a Ubuntu system that has automatic updates will this affect my Wi-Fi?
Yes as new kernels are updated in Ubuntu automatically it will break backports and will need to be reinstalled.
Can I use a Laird WiFi module on Ubuntu?
Laird modules can be used on a Ubuntu system with a kernel version that is supported by Laird backports.
To check, find the kernel version of the Ubuntu system and then check the release notes of the products to see if the latest backports supports that kernel.
Can I use VOUT_3P3 to power VDDIO?
No, if VBAT is 3.6V or greater, this power source should be used for VDDIO_RF, and USB2_AVDD33 if strapped for USB. Otherwise leave this pin disconnected.
Is there a way to extend the shelf life of Laird modules?? If the shelf life cannot be extended in any way, what are the consequences of using modules after shelf life?
The shelf life statements are essentially to prevent mishandling of the product and not storing it properly. If the modules are still sealed in the package, stored at the proper temperature and have not been exposed to moisture they should be fine. However, when working with modules beyond their shelf life you MUST bake the modules before populating the them to your board. Failure to bake the modules could result in the yield rate dropping down lower than expectation due to popcorn or de-lamination on the modules. It is recommended that you follow IPC/JEDEC J-STD-033 which is the general standard for the handling, packing, shipping and use of moisture/reflow sensitive surface mount devices.
Our main concern is around the castellation/pads which solder the module to the board. It is imperative those pads do not get tarnished, as this would cause soldering issues. Humidity can affect solderability as well, as if there is any excess moisture in the solder on the module, during reflow of the module to the board, steam balls can essentially explode the solder and sometimes result in an open circuit (or possibly a short circuit).
As long as all of the moisture handling and temperature guidelines are being followed you will likely have no issues. It is further recommended that when you do the build with modules that have exceeded their shelf life that you start with a handful to perform a test run and do a final test to make sure all is working as expected. As long as there are no issues with the initial test run we would expect that you will not experience any problems.
Become an Ezurio Customer to Gain Exclusive Access to Our Design Experts
- Antenna Scans
- Antenna selection and placement
- Custom antenna design
- Worldwide EMC testing / certifications
- Embedded RF hardware / firmware design
- Cloud architecture and integration
- Mobile application development
- Product & Industrial Design
Buy Now
| Distributor | Part | In Stock | Region | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouser | 453-00083C | 996 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00083R | 0 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00084-K1 | 8 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00084C | 266 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00084R | 0 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00085-K1 | 14 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00085C | 117 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00085R | 0 | North America | Buy Now |
| Mouser | 453-00141 | 93 | North America | Buy Now |
Distributors
| Distributor | Phone Number | Region | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arrow Electronics | 1-855-326-4757 +44 2039 365486 |
APAC, North America, South America, EMEA | Website |
| Avnet | 1-480-643-2000 +44 1628 512900 |
APAC, North America, South America, EMEA | Website |
| Braemac Australia, New Zealand, South East Asia | +61 2 9550 6600 +64 9 477 2148 |
APAC | Website |
| Cal-Chip Connect | 1-215-942-8900 |
North America | Website |
| DigiKey | 1-800-344-4539 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| EBV Elektronik | EMEA | Website | |
| Farlink Technology China, Hong Kong | +86 13266922199 |
APAC | Website |
| Farnell | 1-800-936-198 +44 3447 11 11 22 |
EMEA | Website |
| Future Electronics | 1-800-675-1619 1-514-428-8470 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Glyn | +49-6126-590-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Hy-Line Germany Only | +49 89 614 503 0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Jetronic China, Hong Kong and Taiwan | 852-27636806 |
APAC | Website |
| Laird Connectivity | 1-847-839-6925 +44 1628 858941 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| M2M Germany | +49-6081-587386-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Martinsson | +46 8 7440300 |
EMEA | Website |
| McCoy South East Asia | +65 6515 2988 |
APAC | Website |
| Mouser | 1-800-346-6873 +44 1494 427500 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| RS Components | +852-2421-9898 +44 3457-201201 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Ryoyo Japan | +81-3-3543-7711 |
APAC | Website |
| Solsta UK Only | +44 (0) 1527 830800 |
EMEA | Website |
| Supreme Components International India, South East Asia | +65 6848-1178 |
APAC | Website |
| Symmetry Electronics | 1-866-506-8829 |
North America | Website |
| Tekdis Australia and New Zealand | +61 3 8669 1210 |
APAC | Website |
| Telsys | +972 3 7657666 |
EMEA | Website |
| WPG | +44 1628 958460 |
EMEA | Website |
 Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio
Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio/filters:background_color(white)/2022-10/Sterling-LWB%2B-Family.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2021-10/453-00083.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2021-10/453-00084_0.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2021-10/453-00085_0.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2022-10/Sterling%20LWB%2B%20M.2%20%28453-00141%29-Front-crop.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2019-03/2-4-ghz-flexnotch-rf-antenna.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2018-11/mFlexPIFA-standalone-thumb_0.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2022-05/2.4ghz%20flexpifa.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2022-11/i-FlexPIFA-2.4-EFG2400A-view2.png)
