More Hospitals Adopt Wireless Medical Devices
Published on September 8, 2014

By Jordan Manser, Technical Writer
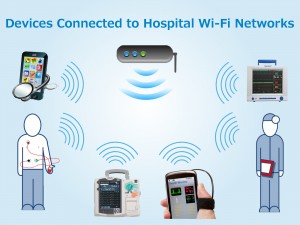
As the world continues to go wireless, healthcare facilities must keep pace in order to provide the best patient care possible. Healthcare providers that leverage wireless medical devices provide increased patient safety, data accuracy, and mobility, resulting in overall improved patient care. Though nearly all hospitals have Wi-Fi, implementing wireless medical devices has been a slow process due to the lack of understanding of Wi-Fi. While it is important to be cautious when it comes to security and patient safety, the more educated hospitals become about Wi-Fi, the more they understand that the risks associated with wireless medical devices can be significantly reduced when the best solution is chosen and the appropriate steps to implement the technology are taken. A real world example of this can be found at the University of Miami.
The University of Miami and its affiliated health organization, UHealth- University of Miami Health System, are implementing a wireless infrastructure upgrade, according to an article in Campus Technology titled, “New Wireless Network to Serve More than 25,000 Devices Per Day at the University of Miami”. In addition to covering 200 buildings and 11 million square feet across the university’s three main campuses, the wireless network will also cover UHealth’s three hospitals and 24 outpatient facilities. The new wireless network will help UHealth achieve their main goals of organization-wide access and mobility, the ability to handle an increasing density of mobile and wireless medical devices, and supporting a BYOD policy.
To achieve these goals, IT personnel must ensure that devices never lose connectivity. Client devices must be able to roam, or switch, from one access point (AP) to another while still maintaining an active network connection. Not all wireless medical devices have the same Wi-Fi mobility capabilities, so it is important for hospital IT professionals to choose wireless medical devices that are embedded with certified Wi-Fi modules that go through the roaming process quickly and seamlessly and come with an arsenal of support services. If the appropriate steps are taken when selecting and integrating wireless medical devices, hospitals can then take advantage of the secure wireless connectivity that Wi-Fi provides.
 Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio
Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio